Welcome to Your Scientific Guide to the Cycle Threshold (CT) Value





Our mission
Our mission is to help students, researchers, clinicians, and molecular biologists understand how CT values are used to interpret diagnostic results, evaluate viral load, and ensure the precision of molecular assays.

What is Cycle Threshold (CT)?
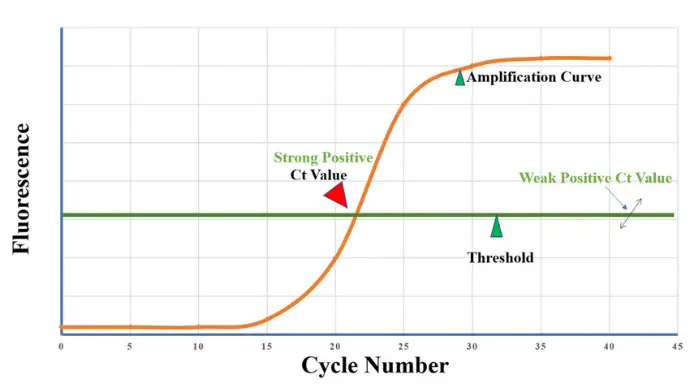
In real-time PCR, every amplification cycle doubles the amount of DNA. The CT value indicates the cycle number at which fluorescence from the amplified DNA exceeds the background level.
Low CT value (15–25) → High amount of target DNA or RNA (high viral load)
High CT value (30–40) → Low amount of target DNA or RNA
Applications of CT Value
01
Clinical Diagnostics:
Detecting viruses such as Human Papillomavirus (HPV), Cytomegalovirus (CMV), and Influenza using RT-qPCR.
02

Molecular Biology:
Research Quantification of gene expression and mRNA transcripts.
03

Forensic Science:
DNA profiling and sample validation.
04

Agricultural Biotechnology:
Detecting pathogens and genetic markers in crops.

How is CT Calculated?
During a qPCR run, fluorescent dyes or probes (like SYBR Green or TaqMan probes) emit signals proportional to the amplified product. The cycle threshold is automatically determined when fluorescence surpasses a defined baseline.
Interpreting CT Values in Clinical Tests
In diagnostic PCR: